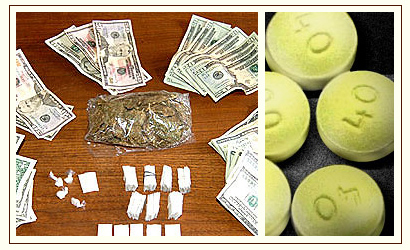
Every element of a crime must be proven beyond a reasonable doubt
Every crime is made up of parts that are called elements. When a person is charged with a crime, the prosecutor is saying that there is sufficient evidence to establish each and every element of the crime beyond a reasonable doubt. The prosecutor does not always get it right. Many criminal cases result in an acquittal because an essential element of a crime has not been established beyond a reasonable doubt. In this ABDO LAW publication, the element of “possession” is explained in relation to drug crimes.
Illegal possession of drugs may constitute a felony
Possession is a necessary element in drug crimes and property crimes (receiving and concealing stolen property). For a person to found guilty of a drug crime, the prosecutor must establish that a person intentionally and knowingly possessed the illegal drugs in question. Most drug crimes are felonies that carry serious criminal penalties which can include possible jail, substantial fines and driver license suspension:
| Drug Crime | Maximum Jail | Maximum Fine |
|---|---|---|
| Possession of MDMA | 10 years | $2,000.00 |
| Possession of methamphetamine | 10 years | $2,000.00 |
| Possession of heroin or cocaine | 4 years | $25,000.00 |
| Possession of analogues | 2 years | $2,000.00 |
In another article, we explain how drug possession crimes in Michigan (including all Macomb County District Courts) can be dismissed pursuant to MCL 3333.7411.
“Possession” is a necessary element in drug crimes
The term possession has different meanings in the criminal justice system. A person may be charged with possession of drugs if he or she has “actual possession” or “construction possession”. Because the term “possession” has different meanings and the potential for different interpretations, it is often the subject of legal arguments in criminal cases.
Historically, actual possession was required for a conviction of a criminal case with the element of possession. In other words, a person could not be charged with a crime unless he was “caught red handed” with the illegal property. In the 1920s era of liquor prohibition, courts expanded criminal possession to include “constructive possession”. Constructive possession does not require an individual to have the physical possession of the illegal property.
Possession does not require ownership: Possession is not the same as ownership. Several criminal laws make it a crime to “possess” something that is forbidden or illegal.
Actual possession is what most of us think of as possession, that is, having physical custody or control of an object. Actual possession, also sometimes called possession in fact, is used to describe immediate physical contact. Frequently, a set of facts clearly indicate that an individual has possession of an object but that he or she has no physical contact with it (constructive possession). To properly deal with these situations, courts have broadened the scope of possession beyond actual possession.
Constructive possession is a legal theory used to extend possession to situations where a person has no hands-on custody of an object. Constructive possession is frequently used in cases involving drugs, guns and stolen property in Michigan criminal cases. Constructive possession, also sometimes called “possession in law,” exists where a person has the ability to control the object even if the person has no physical contact with it. For example, people often keep important papers and other valuable items in a bank safety deposit box. Although they do not have actual physical custody of these items, they do have knowledge of the items and the ability to exercise control over them.
Michigan Cases: Interpretation of constructive possession
People v Nunez (2000): In this case, police a large stash of cocaine in a home occupied by several individuals. Although Mr. Nunez didn’t have the cocaine on his person, he was charged and convicted of possession of cocaine. The police arrived at their conclusion by observing the apartment and its contents. Mr. Nunez had a key for the apartment and stayed at the apartment most of the time. His name was also found on bills within the apartment.
People v Meshell (2005): In this case, police observed a man emerging from a garage in which they later discovered methamphetamine. Upon entering the area, police noticed a strong chemical odor coming from the garage. Mr. Meshell was the only person in the area of the garage and when police ran his record, they discovered past issues with methamphetamine. Because Mr. Meshell had past issues with meth, it was obvious that he knew the smell. He was also the only one in the area at the time police observed him exiting the garage.
People v McKinney (2003): In this case, police entered a home and discovered a large amount of cocaine. Police found crack in drawers containing women’s clothing, and linked the drugs to Ms. McKinney because she was frequently staying at the apartment. By using the drug’s location as evidence, the police were able to successfully charge and convict Ms. McKinney of possession of cocaine.
Do not make common mistakes like talking to the police or consenting to a search. Exercising your right to remain silent cannot be used against you. Also don’t be tricked into giving the police consent to search your vehicle or home. Contact the Abdo Law immediately if you are being investigated or charged with any drug crime.
Free Consultation & Same Day Appointments!
Calls Forwarded to Mobile Phone 7/24/365
Call the ABDO LAW FIRM 24 Hours Phone: (586) 412-5555
 Michigan Criminal Lawyer Blog
Michigan Criminal Lawyer Blog